Switching from IRAF STSDAS SYNPHOT
This section provides basic switcher’s guide for those who are familiar with IRAF STSDAS SYNPHOT. This guide is not meant to be all-inclusive for two reasons:
Some of the SYNPHOT tasks can be reproduced in several different ways using pysynphot.
Not all the SYNPHOT tasks are available in pysynphot.
The agreement of results between these two software were discussed in detail in TSR 2009-01: Pysynphot Commissioning Report (Laidler 2009).
In the tables below:
sprepresents a source spectrumbprepresents a bandpassobsrepresents an observation
Source Spectrum
pysynphot |
SYNPHOT |
|---|---|
S.FileSpectrum(filename) |
spec(filename) |
S.BlackBody(temperature) |
bb(temperature) |
S.FlatSpectrum(val, fluxunits=form) |
unit(val, form) |
S.Powerlaw(refval, expon, fluxunits=form) |
pl(refval, expon, form) |
S.GaussianSource(totflux, mu, fwhm, fluxunits=form) |
em(mu, fwhm, totflux, form) |
S.ArraySpectrum(wave, flux, fluxunits=form) |
N/A |
S.Icat(model, Teff, Z, log_g) |
icat(model, Teff, Z, log_g) |
sp.renorm(val, form, bp) |
rn(sp, bp, val, form) |
sp.redshift(z) |
z(sp, z) |
sp.writefits(filename) |
calcspec sp filename |
plt.plot(sp.wave, sp.flux) |
N/A |
Bandpass
There is no single bandpass method that is equivalent to IRAF STSDAS SYNPHOT
bandpar task, but different commands can be used separately in order to
derive different photometric properties, as tabulated below.
pysynphot |
SYNPHOT |
|---|---|
S.FileBandpass(filename) |
thru(filename) |
S.Box(mu, width) |
box(mu, width) |
S.ObsBandpass(obsmode) |
band(obsmode) |
bp.avgwave() |
bandpar bp photlist=avglam |
bp.efficiency() |
bandpar bp photlist=qtlam |
bp.equivwidth() |
bandpar bp photlist=equvw |
bp.rectwidth() |
bandpar bp photlist=rectw |
bp.photbw() |
bandpar bp photlist=bandw |
bp.throughput.max() |
bandpar bp photlist=tpeak |
bp.thermback() |
thermback obsmode |
bp.writefits(filename) |
calcband bp filename |
plt.plot(bp.wave, bp.throughput) |
plband bp |
Observation
pysynphot |
SYNPHOT |
|---|---|
S.Observation(sp, bp) |
N/A |
obs.countrate() |
calcphot bp sp counts |
obs.effstim(form) |
calcphot bp sp form |
obs.efflam() |
calcphot bp sp flam func=’efflerg’ |
obs.writefits(filename) |
N/A |
plt.plot(obs.binwave, obs.binflux) |
plspec bp sp photlam |
Miscellaneous
pysynphot |
SYNPHOT |
|---|---|
S.Extinction(val, law) |
ebmvx(val, law) |
S.Extinction(val, ‘gal1’) |
ebmv(val) |
S.Waveset(w1, w2, dw) |
genwave filename w1 w2 dw |
Language Parser
pysynphot also has a special parser that can read some of the legacy
SYNPHOT language for spectrum objects. However, the parser cannot perform
legacy commands such as calcphot or bandpar.
The following table lists the available operations:
Parser Syntax |
Pythonic Equivalent |
|---|---|
band(obsmode) |
S.ObsBandpass(obsmode) |
bb(temperature) |
S.BlackBody(temperature) |
box(mu, width) |
S.Box(mu, width) |
ebmvx(val, law) |
S.Extinction(val, law) |
em(mu, fwhm, totflux, form) |
S.GaussianSource(totflux, mu, fwhm, fluxunits=form) |
icat(model, Teff, Z, log_g) |
S.Icat(model, Teff, Z, log_g) |
pl(refval, expon, form) |
S.Powerlaw(refval, expon, fluxunits=form) |
rn(sp, bp, val, form) |
sp.renorm(val, form, bp) |
spec(filename) |
S.FileSpectrum(filename) |
unit(val, form) |
S.FlatSpectrum(val, fluxunits=form) |
z(sp, z) |
sp.redshift(z) |
These are the flux units (form) recognized by the parser
(for wavelength, only Angstrom is accepted):
fnuflamphotnuphotlamcountsabmagstmagobmagvegamagjymjy
These are the reddening laws recognized by the parser.
They are used for the law variable in the ebmvx command above:
gal1gal3smclmcxgal
This example shows how a blackbody can be generated using the parser and the regular Python class. It also shows that they are both the same thing:
>>> from pysynphot import spparser as P
>>> bb1 = P.parse_spec('bb(5000)')
>>> bb2 = S.BlackBody(5000) # Equivalent to bb1
>>> assert bb1.integrate() == bb2.integrate()
Meanwhile, this example shows how to use the parser to apply extinction to a redshifted and renormalized spectrum obtained from a catalog. It also generates the same spectrum using regular Python commands, and compares them:
>>> sp1 = P.parse_spec('ebmvx(0.1, lmc) * z(rn(icat(k93models, 5000, -0.5, 4.4), band(johnson,v), 18, abmag), 0.01)')
>>> sp2 = S.Extinction(0.1, 'lmc') * S.Icat('k93models', 5000, -0.5, 4.4).renorm(18, 'abmag', S.ObsBandpass('johnson,v')).redshift(0.01)
>>> assert sp1.integrate() == sp2.integrate()
Examples
In the examples below, the SYNPHOT commands are preceded by sy>.
They are followed by the pysynphot equivalent in >>>.
Some examples are adapted from SYNPHOT documentation.
IRAF STSDAS SYNPHOT setup:
iraf> stsdas
iraf> hst_calib
iraf> synphot
sy>
Calculate the pivot wavelength and the total flux (in counts/s) of a 5000 K blackbody in the HST/WFPC F555W bandpass. The blackbody spectrum is normalized to have a V magnitude of 18.6:
sy> calcphot "band(wfpc,f555w)" "rn(bb(5000),band(v),18.6,vegamag)" counts
Mode = band(wfpc,f555w)
Pivot Equiv Gaussian
Wavelength FWHM
5467.653 1200.953 band(wfpc,f555w)
Spectrum: rn(bb(5000),band(v),18.6,vegamag)
VZERO (COUNTS s^-1 hstarea^-1)
0. 419.5938
>>> obs = S.Observation(
... S.BlackBody(5000).renorm(18.6, 'vegamag', S.ObsBandpass('v')),
... S.ObsBandpass('band(wfpc,f555w)'))
>>> obs.bandpass.pivot()
5467.6512917540995
>>> obs.countrate()
418.74429418688777
Calculate the total flux (in obmag) of a 5000 K blackbody in the HST/ACS
WFC1 F555W bandpass for \(E(B-V)\) values of 0.0, 0.25, and 0.5:
sy> calcphot "acs,wfc1,f555w" "bb(5000)*ebmv($0)" obmag vzero="0.0,0.25,0.5"
Mode = band(acs,wfc1,f555w)
Pivot Equiv Gaussian
Wavelength FWHM
5361.008 847.9977 band(acs,wfc1,f555w)
Spectrum: bb(5000)*ebmv($0)
VZERO (OBMAG s^-1 hstarea^-1)
0. -10.0087
0.25 -9.1981
0.5 -8.39187
>>> for ebv in (0.0, 0.25, 0.5):
... obs = S.Observation(
... S.BlackBody(5000) * S.Extinction(ebv, 'gal1'),
... S.ObsBandpass('acs,wfc1,f555w'))
... print('{0}\t{1:.4f}'.format(ebv, obs.effstim('obmag')))
0.0 -10.0087
0.25 -9.1981
0.5 -8.3919
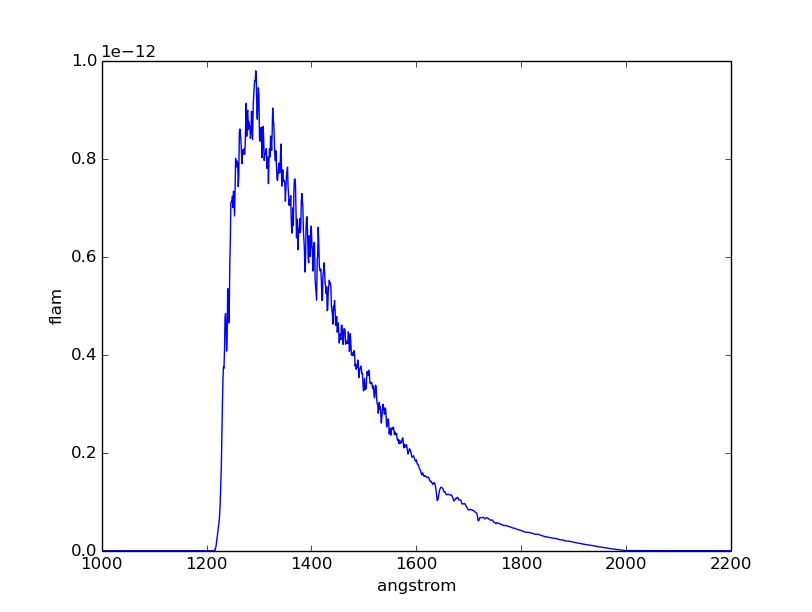
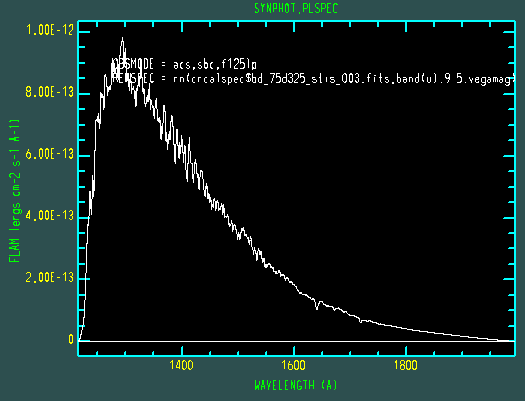
Plot an observation of BD+75 325 using the HST/ACS SBC F125LP bandpass in the
unit of flam. The spectral data for BD+75 325 are stored in
$PYSYN_CDBS/calspec/bd_75d325_stis_003.fits file. Because this spectrum has
been arbitrarily normalized in intensity, we must first renormalize it to its
proper U magnitude of 9.5:
sy> plspec "acs,sbc,f125lp" "rn(crcalspec$bd_75d325_stis_003.fits,band(u),9.5,vegamag)" flam
>>> filename = os.path.join(
... os.environ['PYSYN_CDBS'], 'calspec', 'bd_75d325_stis_003.fits')
>>> obs = S.Observation(
... S.FileSpectrum(filename).renorm(9.5, 'vegamag', S.ObsBandpass('u')),
... S.ObsBandpass('acs,sbc,f125lp'))
>>> obs.convert('flam')
>>> plt.plot(obs.wave, obs.flux)
>>> plt.xlim(1000, 2200)
>>> plt.xlabel(obs.waveunits)
>>> plt.ylabel(obs.fluxunits)